Getting Started
The hevm project is an implementation of the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM) focused on symbolic analysis of EVM bytecode. This essentially means that hevm can try out all execution possibilities of your contract and see it can somehow violate some assertions you have. These assertions can be e.g. the total number of tokens must always be X, some value must never be greater than Y, some value must never overflow, etc.
In some sense, hevm is similar to a fuzzer, but instead of only trying with random values to trigger faults, it instead computes whether a fault is possible. If it is possible, it gives an example call to trigger the fault, and if it isn't possible, it mathematically proves it so, and tells the user the contract is safe. Note that while great pains have gone into making sure hevm's results can be trusted, there can always be bugs in hevm or the libraries and tools it uses.
Hevm can not only be used to find bugs in programs, but can also help to make sure that two programs behave equivalently from the outside. This may be advantageous when one may be more efficient (use less gas) to execute, but harder to reason about. This can be done via (equivalence checking)[#equivalence-checking] where hevm either proves that the behaviour of the two bytecodes is the same, or gives inputs where they differ.
Practical Scenario
Let's say we have a function that allows transfer of money, but no balance can be larger than or equal to 100. Let's see the contract and its associated check:
pragma solidity ^0.8.19;
import "forge-std/Test.sol";
contract MyContract is Test {
mapping (address => uint) balances;
function prove_add_value(address recv, uint amt) public {
require(balances[recv] < 100);
if (balances[recv] + amt > 100) {
revert();
}
balances[recv] += amt;
assert(balances[recv] < 100);
}
}
Notice that this function has a bug: the require and the assert both check
for <, but the if checks for >, which should instead be >=. Let's see
if hevm can find this bug. In order to do that, we have to prepend the
function name with prove_, which we did.
Building
We now need a copy of hevm (see
releases) and the SMT solver z3,
which can be installed e.g. with apt-get on ubuntu/debian or homebrew on Mac,
and a copy of Foundry:
$ sudo apt-get install z3 # install z3
$ curl -L https://foundry.paradigm.xyz | bash # install foundryup
$ foundryup # install forge and other foundry binaries
$ mkdir mytest && cd mytest
$ wget https://github.com/argotorg/hevm/releases/download/release/0.55.1/hevm-x86_64-linux
$ chmod +x ./hevm-x86_64-linux
$ forge init .
$ cat <<EOF > src/contract.sol
pragma solidity ^0.8.19;
import "forge-std/Test.sol";
contract MyContract is Test {
mapping (address => uint) balances;
function prove_add_value(address recv, uint amt) public {
require(balances[recv] < 100);
if (balances[recv] + amt > 100) {
revert();
}
balances[recv] += amt;
assert(balances[recv] < 100);
}
}
EOF
$ forge build --ast
[⠊] Compiling...
[⠒] Compiling 1 files with 0.8.19
[⠢] Solc 0.8.19 finished in 14.27ms
Compiler run successful!
Finding the Bug
Now let's run hevm to see if it finds the bug:
$ hevm test --solver z3
Running 1 tests for src/contract.sol:MyContract
[FAIL] prove_add_value(address,uint256)
Counterexample:
result: Revert: 0x4e487b710000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000001
calldata: prove_add_value(0x0000000000000000000000000000000000000000,100)
Fixing the Bug
This counterexample tells us that when sending exactly 100 to an empty account, the new
balance will violate the < 100 assumption. Let's fix this bug, the new prove_add_value
should now say:
function prove_add_value(address recv, uint amt) public {
require(balances[recv] < 100);
if (balances[recv] + amt >= 100) {
revert();
}
balances[recv] += amt;
assert(balances[recv] < 100);
}
Let's re-build with forge and check with hevm once again:
$ forge build --ast
[⠰] Compiling...
[⠔] Compiling 1 files with 0.8.19
[⠒] Solc 0.8.19 finished in 985.32ms
Compiler run successful!
$ hevm test --solver z3
Running 1 tests for src/contract.sol:MyContract
[PASS] prove_add_value(address,uint256)
We now get a PASS. Notice that this doesn't only mean that hevm couldn't find
a bug within a given time frame. Instead, it means that there is surely no call
to prove_add_value such that our assertion can be violated. However, it does
not check for things that it was not asked to check for. In particular, it
does not check that e.g. the sender's balance is decremented. There is no such
test and so this omission is not detected.
Capabilities
- Symbolic execution of solidity tests written using
ds-test(a.k.a "foundry tests"). This allows one to find all potential failure modes of a function. - Fetch remote state via RPC so your tests can be rooted in the real-world, calling out to other, existing contracts, with existing state and already deployed bytecode.
- Prove equivalence of two different bytecode objects such as two functions or even entire contracts.
History
Hevm was originally developed as part of the dapptools project, and was forked to this repo by the Formal Verification team at the Ethereum Foundation in August 2022.
Quick Installation Guide
To fastest way to start using hevm is to install Foundry, e.g. via
curl -L https://foundry.paradigm.xyz | bash
Next, you need to have either Z3 or cvc5 installed. Often, these can be installed via:
$ sudo apt-get install z3 cvc5
or similar for Linux. For Mac:
brew install z3
brew install --cask cvc5
If you installed cvc5 and want to use it, you will need to pass the flag "--solver cvc5". The z3 solver is default, but cvc5 is often faster, so you may want to try it out.
Finally, download the static hevm binary from the GitHub repository for your platform and put it in your path so it can be executed via typing "hevm".
How to Check if it Works
Once you have the above, and you have forge installed and a forge-based project
at hand, re-build it with --ast and run the tests with hevm:
$ forge clean
$ forge build --ast
[⠒] Compiling...
[⠆] Compiling 34 files with 0.8.19
[⠔] Solc 0.8.19 finished in 2.12s
Compiler run successful.
$ hevm test
Checking 1 function(s) in contract src/contract-pass.sol:MyContract
[RUNNING] prove_pass(address,uint256)
[PASS] prove_pass(address,uint256)
See Forge std-test tutorial for details.
Note that Foundry provides the solidity compiler, hence there is no need to install solidity separately.
When to use Symbolic Execution
In the cryptocurrency world, it is exceedingly easy to lose a lot of assets due to bugs. While fuzz testing can help find potential issues with digital contracts, it is a tool that can only execute the program concretely, one execution at a time. In contrast, Symbolic Execution can execute all potential values in a decision path "in one go", creating a symbolic expression out of a path, and checking whether it can trigger a fault. Hence, Symbolic Execution tends to be more efficient at finding bugs than fuzzing when the bugs are rare, or explicitly (i.e. maliciously) hidden. Symbolic Execution can also prove that no postcondition can be violated, increasing the overall confidence in the contract. Note, however, that Symbolic Execution does not automatically generate postconditions for well-known bug classes like static code analysis tools do. Instead, these postconditions, and their sometimes associated preconditions, need to be explicitly written.
Fuzzing versus Symbolic Execution
Fuzzing tests usually have a set of (sometimes implicit) pre- and postconditions, but the actual action (e.g. function call) is performed by an external entity, the fuzzer. For C/C++ fuzzing, the implicit postcondition is often e.g. that the system does not throw a segmentation fault. For EVM bytecode, postconditions need to be explicit. Let's see an example:
// SPDX-License-Identifier: MIT
pragma solidity ^0.8.19;
import "forge-std/Test.sol";
contract MyContract is Test {
uint balance;
function test_overflow(uint amt) public {
unchecked {
balance += amt;
}
assert(balance >= amt);
}
}
This function is easy to break by picking an amt that overflows balance,
so that the postcondition balance > amt will not hold. A
fuzzer finds this kind of bug very
easily. However, fuzzers have trouble finding bugs that are either specifically
hidden (e.g. by a malicious developer), or that have a complicated code path
towards them. Let's see a simple one:
// SPDX-License-Identifier: MIT
pragma solidity ^0.8.19;
import "forge-std/Test.sol";
contract MyContract is Test {
uint balance;
function prove_multiply(uint amt, uint amt2) public {
require(amt != 1);
require(amt2 != 1);
require(amt < amt2);
uint tmp;
tmp = amt * amt2;
if (tmp == 119274257) balance = 1337;
else balance += tmp;
assert(balance >= tmp);
}
}
Calling this contract with amt = 9479 and amt2 = 12583 will set the balance
to 1337 which is less than amt*amt2, breaking the postcondition. However, a
fuzzer, e.g. Echidna will likely not find
those numbers, because uint has a potential range of 2**256 and so it'd be
looking for a needle in a haystack, when looking randomly. Here's how to run
Echidna on the multiplication test:
// SPDX-License-Identifier: MIT
pragma solidity ^0.8.19;
contract MyContract {
// the rest is the same
}
Then run:
echidna --test-mode assertion src/multiply-test.sol
Echidna will terminate after 50k runs, with all tests passing. Notice that the difference here, compared to the previous example, is that the overflow example has many different inputs that can break the postcondition, whereas here only one can.
Hevm finds the bug in both of these functions. This is because hevm (and symbolic execution frameworks in general) try to find the bug via proof-directed search rather than using random inputs. In hevm, we try to prove that there are no inputs to the test case such that given the preconditions, the postconditions can be broken. While trying to construct this mathematical proof, hevm finds a countereexample, an input that breaks the postconditions:
$ hevm test
Checking 1 function(s) in contract src/multiply-test.sol:MyContract
[RUNNING] prove_multiply(uint256,uint256)
[FAIL] prove_multiply(uint256,uint256)
Counterexample:
result: Revert: 0x4e487b710000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000001
calldata: prove_multiply(9479,12583)
Checking 1 function(s) in contract src/overflow-test.sol:MyContract
[RUNNING] prove_overflow(uint256)
[FAIL] prove_overflow(uint256)
Counterexample:
result: Revert: 0x4e487b710000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000001
calldata: prove_overflow(00000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000100000000000000000182dad8c17bd5e89e8043a08ada90a6d5efdee4425f85cb863109783e158ba4fba908a0e6fae6c6b51002)
Similarities and Differences to Other Tools
Fuzzers are exceedingly fast and efficient when there are many potential faults with a function/contract, or if the faults are of a type that's easy to search for (e.g. off-by-one). However, they rarely, if ever, find cases where the bug is hidden deep in the branch logic, or needs very specific input parameters. Hence, it is best to use fuzzers at first to find easy-to-find bugs, as fuzzers are very efficient at that. Then, once the tests pass the fuzzer, it is recommended to use a symbolic execution engine such as hevm.
hevm is similar to Halmos and Kontrol in its approach. However, it is quite different from static code analysis tools such as Oyente, Slither, and Mythril. While these 3 tools typically use some form of symbolic execution to try to validate their results, their main method of operation is not via symbolic execution, and they can, and do, report false positives.
Notice that static code analysis tools can find bugs that the author(s) didn't write a test case for, as they typically have a (large) set of preconfigured test-cases that they can report on, if they can find a way to violate them. Hence, it may be valuable to run static analysis tools alongside symbolic execution tools such as hevm.
Finally, SMTChecker may also be interesting to run alongside hevm. SMTChecker is very different from both approaches detailed above. While SMTChecker is capable of reliably finding both reentrancy and loop-related bugs, the tools above can only do so on a best effort basis. Hevm often reports a warning of incompleteness for such problems, while static code analysis tools either report potential positives or may even not discover them at all.
| Tool | Approach | Primary Method | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| hevm | Symbolic analysis of EVM bytecode | Symbolic execution | Focuses on exploring all execution possibilities, identifying potential assertion violations, and optimizing gas usage. Can prove equivalence between bytecodes. |
| Halmos | Similar to hevm | Not specified | Approach similar to hevm, but the document does not detail specific methodologies or differences. |
| Kontrol | Similar to hevm | Not specified | Approach similar to hevm, with a focus presumably on symbolic analysis as well, but further details are not provided in the document. |
| Oyente | Static code analysis | Partial symbolic execution | Uses symbolic execution to validate results but primarily relies on static analysis. Can report false positives. |
| Slither | Static code analysis | Partial symbolic execution | Similar to Oyente, uses static analysis as its main method, complemented by symbolic execution for validation. Known for reporting false positives. |
| Mythril | Static code analysis | Partial symbolic execution | Combines static code analysis with symbolic execution for result validation. Like Oyente and Slither, can report false positives. |
| SMTChecker | Different from both hevm and static code analysis tools | SMT solving | Capable of finding reentrancy and loop-related bugs reliably, which other tools might miss or report incompletely. Offers a distinct approach from symbolic execution. |
Limitations and Workarounds
Symbolic execution in general, and hevm in particular, have a number of known limitations. Many of these limitations can be worked around without too much effort. This document describes some of the most common limitations and workarounds.
Loops and recursion
The most important issue related to symbolic execution is to do with loops and recursion. For example, the following code is hard to deal with in a symbolic context:
function loop(uint n) {
for(uint i = 0; i < n; i++) {
mystate[i]++;
}
}
When such a function is called, and n is a symbolic parameter (e.g. parameter
to a function prove_, such as prove_correct(uint n)), hevm would need to
create a new execution path for each potential value of n, which can be very
large. The same principle applies to recursion, where the depth of the
recursion may be unbounded or bounded only by a potentially very large number.
Hence, hevm only explores loops and recursions up to fixed depth k, a
parameter that can be adjusted from the command line via the --max-iterations k parameter. Whenever the limit is hit, hevm warns of the incomplete exploration:
WARNING: hevm was only able to partially explore the call prefix 0x[...] due to the following issue(s):
- Max Iterations Reached in contract: 0x[...] pc: [...]
In general, the workaround suggested is to try to write code without loops, if
possible, or to have a limit on the number of iterations. For example, by using
max(k,n) instead of n in the loop condition, where k is a fixed number.
Unbounded loops are a problem for digital contracts, as they may be forced by
an attacker to exhaust gas, thereby potentially e.g. deadlocking the contract.
This can lock in (large) funds, which can be a very serious issue. Hence,
limiting loop iterations is a good practice in general -- not only for symbolic
execution.
Best Practices:
- Try to write code without loops, if possible.
- Use
max(k,n)instead ofnin the loop condition, wherekis a fixed number. - Avoid unbounded loops to prevent potential gas exhaustion attacks
Gas costs
Gas is hard to symbolically track, due to certain opcodes, such as SLOAD, having different cost depending on the parameters to the opcode. Many symbolic execution systems, including hevm, solve this by not fully tracking gas. This means that hevm may report that an assertion failure can occur through a particular execution trace, but that trace would cost more to execute than the allowable gas limit.
In general, it is possible to check whether the issue can be hit by running the hevm-provided counterexample in a concrete execution setting, thereby filtering out false positives. However, it is strongly advisable to fix potential issues that are only guarded due to gas exhaustion, as they may become exploitable in the future, when gas costs change.
Best Practices:
- Don't rely on gas exhaustion as a security mechanism.
- Check potential issues by running the hevm-provided counterexample in a concrete execution setting.
Symbolic arguments to certain EVM opcodes
When a symbolic argument is passed to an EVM opcode that hevm cannot deal with symbolically, an error is raised. There are number of such EVM opcodes, for example JUMP, JUMPI, CALL, CALLCODE, DELEGATECALL, STATICCALL, CREATE, CREATE2, SELFDESTRUCT, etc. If any of these are called with an argument that is symbolic, hevm raises an error, such as:
WARNING: hevm was only able to partially explore the call prefix 0x[...] due to the following issue(s):
- Attempting to transfer eth to a symbolic address that is not present in the state
There is no single workaround for this class of issues, as it depends on the
specific circumstances of the code. In general, we suggest trying to concretize
the call to the code, such that only what is truly needed to be symbolic is
left symbolic. For example, you may be able to force partial concrete execution via
require() statements, thereby concretizing the potential symbolic value. Similarly,
dynamically computed JUMP destinations can be avoided via pre-computed jump tables, etc.
Best Practices:
- Use
require()statements to concretize symbolic values - Avoid dynamically computed jumps -- use pre-computed jump-tables, if neccesary
Jumping into symbolic code
Jumping into symbolic code is not supported by hevm. This can happen when, e.g. a function creates a contract based on a symbolic value, and then jumps into the code of that contract. In these cases, you will get a warning like the following:
WARNING: hevm was only able to partially explore the call prefix 0x[...] due to the following issue(s):
- Encountered a jump into a potentially symbolic code region while executing initcode. pc: [...] jump dst: [...]
For these cases, we suggest concretizing the call that creates the contract, such that the bytecode created and later jumped to, is not symbolic.
Setting block number
The roll(uint256)
cheatcode can
be used to set the block number in the current EVM state. However, it does not
alter the block number that the RPC calls use. For that, one must use the
--number command line option. Hence, it is not possible to dynamically change
what block number the RPC calls fetch from, other than by restarting the hevm
process with a different block number.
Completeness Warnings and False Positives
hevm attempts to give no false negatives without warnings, but can sometimes
give false positives. Whenever hevm could not prove the absence of negatives,
it prints a warning [WARN]. While hevm attempts to give no false negatives,
it can, in rare occasions, give false positives, indicated by [not reproducible]. This section explains why these happen, and how to interpret
them.
Completeness Warnings
hevm gives a completeness warning to indicate that it had to give up exploration during symbolic execution. Hence, it may be possible that some assertion violations can be violated, but hevm could not explore that path. Hence, this warning is an indication that there may be errors in the contract, but hevm was not able to find them.
These warnings are prefixed with [WARN] and are collated together with the text
hevm was only able to partially explore XYZ due to: and can be either:
- error(s) such as SMT solver internal errors, or SMT translation issues related to dynamic datastructures
- unknown result(s) from the SMT solver, such as timeouts
- partial executions such as missing implementation of a precompile, cheatcode, etc.
Partial executions are the most common cause of incompleteness. They can be due to:
- Unexpected symbolic argument to an opcode For example, if a symbolic address is given to
a
CALLinstruction, hevm will not be able to determine which contract is being called, and hence will not be able to explore that path. This can be alleviated with the option--only-deployed, which will restrict the analysis to only the contracts that are deployed during thesetUp()phase of the test. - Maximum iterations reached This happens when we have too many iterations in a loop,
and we have reached the maximum number of iterations allowed. This can be configured
with the
--max-iterationsoption. - Jump into symbolic code This can happen in case the contract generates code at runtime, deploys it, and jumps into it. hevm does not support this, and will give up exploration.
- Branch too deep This happens when the call depth has been limited via the
--max-depthoption, and hevm has reached that limit during exploration. - Cheat code missing This happens when a cheatcode is called that is not yet implemented in hevm.
False Positives
hevm attempts to validate every counterexample it can find. In case the
counterexample validates, it marks it via [validated]. In case there is an
error in validating the counterexample, it marks it via [error attempting to reproduce...]. When the counterexample cannot be validated, it marks it via
[not reproducible].
False positives can happen in two different scenarios. Firstly, in some cases, hevm attempts to overapproximate the behaviour of the EVM, so that it doesn't have to give up exploration. However, this overapproximation can lead to behaviour that is not actually possible in the real world. This kind of overapproximation happens mostly with a STATICCALL to an unknown address.
Secondly, false positives can happen, because hevm approximates the Keccak (i.e. SHA3) hash function via a so-called uninterpreted function. This means that hevm does not precisely model the Keccak function, but instead treats it as a black box. This can lead to Keccak hash pairs that are not possible in the real world.
Forge std-test Usage Tutorial
First, install foundry:
curl -L https://foundry.paradigm.xyz | bash
foundryup
Then set up a forge project with forge init:
mkdir myproject
cd myproject
forge init --no-git .
Now, let's create a file src/example-test.sol with some simple code.
Test cases must be prepended with prove_ and the testing contract must
inherit from Test from Forge's standard test
library. So let's import Test:
import {Test} from "forge-std/Test.sol"; and then inherit from it via
is Test. This allows hevm to discover the test cases it needs
to run:
pragma solidity ^0.8.19;
import {Test} from "forge-std/Test.sol";
contract Example is Test {
function prove_mytest() public {
// (1) environment setup, preconditions
// (2) calls to test
// (3) postcondition checks
}
}
Once you have written such a test case, you need to compile with forge build --ast
(see forge documentation for more
details) and then:
$ forge build --ast
$ hevm test --match "prove_mytest"
Checking 1 function(s) in contract src/example-test.sol:Example
[RUNNING] prove_mytest(uint256)
[PASS] prove_mytest(uint256)
Here, hevm discovered the test case, and automatically checked it for
violations. If hevm is not in the global path, you can run hevm
from wherever it is installed, and specify the root of the foundry project,
like so:
./hevm test --root /path/to/foundry/project
The --match ... options is used to specify which test case(s) to run,
and it accepts a regular expression.
Setting Up Test Context
Tests usually need to set up the environment in a particular way, such
as contract address, storage, etc. This can be done via Cheat Codes that
can change the address of the caller, set block number, etc. See Cheat
Codes below for a range of cheat codes supported. Cheat Codes
are a standard method used by other tools, such as
Foundry, so you should be able to re-use your
existing setup. An example setup could be put into src/setup-test.sol:
pragma solidity ^0.8.19;
import {Test} from "forge-std/Test.sol";
contract MyVault {
mapping(address => uint256) public balance;
function deposit() external payable {
balance[msg.sender] += msg.value;
}
}
contract MySetupTest is Test {
MyVault vault;
function setUp() public {
vault = new MyVault();
address user1 = address(42);
vm.deal(user1, 7 ether);
vm.prank(user1);
vault.deposit{value: 7 ether}();
}
function prove_correct(uint8 amt) public {
address k = address(42);
uint pre = vault.balance(k);
assert(pre == 7 ether);
vm.prank(k);
vault.deposit{value: amt}();
assert(vault.balance(k) == pre + amt);
}
}
The setUp function is called before each test case, and can be used to
set up the environment. In this case, we create a new vault, and deposit 7
ether into it for address 42: the vm.deal function sets the balance of the
user to 7 ether, and the vm.prank function sets the caller to address 42. This
should now pass our test:
$ hevm test
Checking 1 function(s) in contract src/setup-test.sol:MySetupTest
[RUNNING] prove_correct(uint8)
[PASS] prove_correct
In general, the test should check the postconditions, e.g. the state of the contract after the call(s) are complete. It should also check that invariants of the contract, such as total number of tokens, are not violated. You can read more about testing and cheat codes in the (Foundry Book)[https://book.getfoundry.sh/forge/cheatcodes] and you can see the hevm-supported cheat codes below.
Understanding Counterexamples
When hevm discovers a failure, it prints an example call how to trigger the
failure. Let's write the following simple solidity code to
src/contract-fail.sol:
pragma solidity ^0.8.19;
import {Test} from "forge-std/Test.sol";
contract MyContract is Test {
mapping (address => uint) balances;
function prove_single_fail(address recv, uint amt) public {
require(balances[recv] < 100);
if (balances[recv] + amt > 100) { revert(); }
balances[recv] += amt;
assert(balances[recv] < 100);
}
}
When compiling our foundry project, we must either always pass the --ast flag
to forge build, or, much better, set the ast = true flag in the
foundry.toml file:
ast = true
In case neither --ast was passed, nor ast = true was set in the
foundry.toml file, when running hevm, we will get an error such as:
Error: unable to parse Foundry project JSON: [...]/out/Base.sol/CommonBase.json Contract: "CommonBase"
In these cases, issue forge clean and run forge build --ast again.
Once the project has been correctly built, we can run hevm test, and get:
$ hevm test
Checking 1 function(s) in contract src/contract-fail.sol:MyContract
[RUNNING] prove_single_fail(address,uint256)
[FAIL] prove_single_fail(address,uint256)
Counterexample:
result: Revert: 0x4e487b710000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000001
calldata: prove_single_fail(0x0000000000000000000000000000000000000000,100)
Here, hevm provided us with a calldata, where the receiver happens to be the
zero address, and the value sent is exactly 100. This indeed is the boundary
condition where the function call fails. The function should have had a >=
rather than a > in the if. Notice that in this case, while hevm filled in
the address to give a complete call, the address itself is irrelevant,
although this is not explicitly mentioned.
Starting State is Always Concrete
In test mode, hevm runs with the starting state set to concrete values, as
dictated by the setUp() function explained above. This
means that with the solidity-generated default constructor of contracts, state
variables will be zero (unless set otherwise by setUp()),
and arrays and mappings will be empty. If you need a
different starting state, such as e.g. tokens already distributed to some
addresses, you can set that up in the setUp() phase of your test.
In case you need a symbolic starting state, see the Symbolic execution
tutorial. Note that if all you need is a
symbolic calldata, then you don't need to run hevm in symbolic mode, you can
simply run hevm test and hevm will provide you with a symbolic calldata.
Test Cases that Must Always Revert
Hevm assumes that a test case should not always revert. If you have such a test case, hevm will warn you and return a FAIL. For example this toy contract:
pragma solidity ^0.8.19;
import {Test} from "forge-std/Test.sol";
contract MyContract is Test {
uint256 cntr;
function prove_allrevert(uint256 val) public {
if(val < 0) {
unchecked { cntr = val; }
revert();
} else revert();
}
}
When compiled with forge and then ran under hevm with hevm test, hevm returns:
Checking 1 function(s) in contract src/contract-allrevert.sol:MyContract
[RUNNING] prove_allrevert(uint256)
[FAIL] prove_allrevert(uint256)
Reason:
No reachable assertion violations, but all branches reverted
Prefix this testname with `proveFail` if this is expected
This is sometimes undesirable. In these cases, prefix your contract with
proveFail_ instead of prove_:
pragma solidity ^0.8.19;
import {Test} from "forge-std/Test.sol";
contract MyContract is Test {
uint256 cntr;
function proveFail_allrevert_expected(uint256 val) public {
if(val < 0) {
unchecked {
cntr = val;
cntr += 1;
}
revert();
}
else revert();
}
}
When this is compiled with forge and then checked with hevm, it leads to:
Checking 1 function(s) in contract src/contract-allrevert-expected.sol:MyContract
[RUNNING] proveFail_allrevert_expected(uint256)
[PASS] proveFail_allrevert_expected(uint256)
Which is now the expected outcome.
Panic Codes
Solidity generates different panic codes for different kinds of issues. The list of panic codes returned by Solidity are:
- 0x00: Used for generic compiler inserted panics, such as e.g. wrong ABI encoding, or if the ABI decoder fails to decode a value.
- 0x01: If you call assert with an argument that evaluates to false.
- 0x11: If an arithmetic operation results in underflow or overflow outside of an unchecked { ... } block.
- 0x12; If you divide or modulo by zero (e.g. 5 / 0 or 23 % 0).
- 0x21: If you convert a value that is too big or negative into an enum type.
- 0x22: If you access a storage byte array that is incorrectly encoded.
- 0x31: If you call .pop() on an empty array.
- 0x32: If you access an array, bytesN or an array slice at an out-of-bounds or negative index (i.e. x[i] where i >= x.length or i < 0).
- 0x41: If you allocate too much memory or create an array that is too large.
- 0x51: If you call a zero-initialized variable of internal function type.
Of these, hevm test will only report counterexamples for 0x1, or for custom errors that
developers define, such as:
error InsufficientBalance(uint256 requested, uint256 available);
....
uint reqested = ...;
uint available = ...;
if (requested > available) {
revert InsufficientBalance(requested, available);
}
Notice that for panic codes, the returned counterexample will produce a return whose first 4 bytes will be:
$ cast keccak "Panic(uint256)" | cut -c 1-10
0x4e487b71
And if it's a custom error, the first 4 bytes will be:
$ cast keccak "Error(string)" | cut -c 1-10
0x08c379a0
Supported Cheat Codes
Since hevm is an EVM implementation mainly dedicated to testing and
exploration, it features a set of "cheat codes" which can manipulate the
environment in which the execution is run. These can be accessed by calling
into a contract (typically called Vm) at address
0x7109709ECfa91a80626fF3989D68f67F5b1DD12D, which happens to be keccak("hevm cheat code"),
implementing the following methods:
| Function | Description |
|---|---|
function prank(address sender) public | Sets msg.sender to the specified sender for the next call. |
function startPrank(address sender) public | Sets msg.sender to the specified sender until stopPrank() is called. |
function stopPrank() public | Resets msg.sender to the default sender. |
function deal(address usr, uint amt) public | Sets the eth balance of usr to amt. Note that if usr is a symbolic address, then it must be the address of a contract that has already been deployed. This restriction is in place to ensure soundness of our symbolic address encoding with respect to potential aliasing of symbolic addresses. |
function store(address c, bytes32 loc, bytes32 val) public | Sets the slot loc of contract c to val. |
function warp(uint x) public | Sets the block timestamp to x. |
function roll(uint x) public | Sets the block number to x. |
function assume(bool b) public | Add the condition b to the assumption base for the current branch. This functions almost identically to require. For most users, require is preferable. However, in case you wish to understand & modify the internal IR of hevm, you may want to use assume. |
function load(address c, bytes32 loc) public returns (bytes32 val) | Reads the slot loc of contract c. |
function sign(uint sk, bytes32 digest) public returns (uint8 v, bytes32 r, bytes32 s) | Signs the digest using the private key sk. Note that signatures produced via hevm.sign will leak the private key. |
function addr(uint sk) public returns (address addr) | Derives an ethereum address from the private key sk. Note that hevm.addr(0) will fail with BadCheatCode as 0 is an invalid ECDSA private key. |
function ffi(string[] calldata) external returns (bytes memory) | Executes the arguments as a command in the system shell and returns stdout. Expects abi encoded values to be returned from the shell or an error will be thrown. Note that this cheatcode means test authors can execute arbitrary code on user machines as part of a call to dapp test, for this reason all calls to ffi will fail unless the --ffi flag is passed. |
function createFork(string calldata urlOrAlias) external returns (uint256) | Creates a new fork with the given endpoint and the latest block and returns the identifier of the fork. |
function selectFork(uint256 forkId) external | Takes a fork identifier created by createFork and sets the corresponding forked state as active. |
function activeFork() external returns (uint256) | Returns the identifier of the current fork. |
function label(address addr, string calldata label) external | Labels the address in traces |
Equivalence Checking Tutorial
Equivalence checking allows to check whether two bytecodes do the same thing under all input circumstances. This allows to e.g. create two functions, one that is known to be good, and another that uses less gas, but is hard to check for correctness. Then, with equivalence checking, one can check whether the two behave the same.
The notion of equivalence in hevm is defined as follows. Two contracts are equivalent if for all possible calldata and state, after execution has finished, their observable storage state is equivalent and they return the same value. In particular, the following is NOT checked when checking for equivalence:
Note that in the Solidity ABI, the calldata's first 4 bytes are the function selector which decide which function is being called, along with the potential fallback function mechanism. Hence, treating calldata as symbolic covers all possible function calls, including fallback functions. While not all contracts follow the Solidity ABI, since hevm's symbolic equivalence checker does not distinguish between function selector and function parameter bytes in the calldata, it will still correctly check the equivalence of such non-conforming contracts.
Finding Discrepancies
Let's see this toy contract, in file contract1.sol:
//SPDX-License-Identifier: MIT
pragma solidity ^0.8.19;
contract MyContract {
mapping (address => uint) balances;
function my_adder(address recv, uint amt) public {
if (balances[recv] + amt >= 100) { revert(); }
balances[recv] += amt;
}
}
And this, slightly modified one, in file contract2.sol:
//SPDX-License-Identifier: MIT
pragma solidity ^0.8.19;
contract MyContract {
mapping (address => uint) balances;
function my_adder(address recv, uint amt) public {
if (balances[recv] + amt >= 100) { revert(); }
balances[recv] += amt/2;
balances[recv] += amt/2;
}
}
Let's ask hevm to compare the two:
$ hevm equivalence \
--code-a $(solc --bin-runtime "contract1.sol" | tail -n1) \
--code-b $(solc --bin-runtime "contract2.sol" | tail -n1)
Found 90 total pairs of endstates
Asking the SMT solver for 58 pairs
Reuse of previous queries was Useful in 0 cases
Not equivalent. The following inputs result in differing behaviours:
-----
Calldata:
0xafc2c94900000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000023
Storage:
Addr SymAddr "entrypoint": [(0x0,0x10)]
Transaction Context:
TxValue: 0x0
This tells us that with a value of 0x23 being sent, which corresponds
to 35, the two are not equivalent. This is indeed the case: one will add 35 div 2 = 17 twice, which is 34, the other will add 35.
Fixing and Proving Correctness
Let's fix the above issue by incrementing the balance by 1 in case it's an odd value. Let's call this contract3.sol:
//SPDX-License-Identifier: MIT
pragma solidity ^0.8.19;
contract MyContract {
mapping (address => uint) balances;
function my_adder(address recv, uint amt) public {
if (balances[recv] + amt >= 100) { revert(); }
balances[recv] += amt/2;
balances[recv] += amt/2;
if (amt % 2 != 0) balances[recv]++;
}
}
Let's check whether this new contract is indeed equivalent:
$ hevm equivalence \
--code-a $(solc --bin-runtime "contract1.sol" | tail -n1) \
--code-b $(solc --bin-runtime "contract3.sol" | tail -n1)
Found 108 total pairs of endstates
Asking the SMT solver for 74 pairs
Reuse of previous queries was Useful in 0 cases
No discrepancies found
Hevm reports that the two are now equivalent, even though they clearly don't consume the same amount of gas and have widely different EVM bytecodes. Yet for an outside observer, they behave the same. Notice that hevm didn't simply fuzz the contract and within a given out of time it didn't find a counterexample. Instead, it proved the two equivalent from an outside observer perspective.
Dealing with Already Compiled Contracts
If the contracts have already been compiled into a hex string, you can paste
them into files a.txt and b.txt and compare them via:
$ hevm equivalence --code-a "$(<a.txt)" --code-b "$(<b.txt)"
You can also copy-paste the contents of the hex strings directly into the command line, although this can become cumbersome:
$ hevm equivalence --code-a "6080604052348015600e575f80fd5b50600436106026575f3560e01c8063881fc77c14602a575b5f80fd5b60306032565b005b5f600190506002811460455760446048565b5b50565b7f4e487b71000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000005f52600160045260245ffdfea26469706673582212208c57ae04774d9ebae7d1d11f9d5e730075068bc7988d4c83c6fed85b7f062e7b64736f6c634300081a0033" --code-b "6080604052348015600e575f80fd5b50600436106030575f3560e01c806385c2fc7114603457806386ae330914603c575b5f80fd5b603a6044565b005b60426055565b005b60025f541460535760526066565b5b565b60035f541460645760636066565b5b565b7f4e487b71000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000005f52600160045260245ffdfea2646970667358221220bd2f8a1ba281308f845e212d2b5eceab85e029909fa2409cdca7ede039bae26564736f6c634300081a0033"
Working with Raw Bytecode
When doing equivalence checking, the returndata of the two systems are compared, and the calldata is set to be symbolic. This allows us to compare raw bytecode as well -- the code does not need to adhere to the Solidity ABI.
The following contract is written in raw assembly. It takes the 1st byte of the calldata, multiplies it by 0, and stores it in memory, then returns this value:
PUSH1 0x00
CALLDATALOAD
PUSH1 0x00
MUL
PUSH1 0x00
MSTORE
PUSH1 0x01
PUSH1 0x00
RETURN
This can be compiled into bytecode via e.g. evm.codes,
which allows us to both simulate this, and to get a bytecode for it:
60003560000260005260016000f3. Notice that since anything multiplied by 0 is
zero, for any calldata, this will put 0 into the returndata.
Let's compare the above code to an assembly contract that simply returns 0:
PUSH32 0x0
PUSH1 0x00
MSTORE
PUSH1 0x01
PUSH1 0x00
RETURN
This second contract compiles to:
7f000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000060005260016000f3.
Let's check whether the two are equivalent:
$ hevm equivalence --code-a "60003560000260005260016000f3" --code-b "7f000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000060005260016000f3"
Found 1 total pairs of endstates
Asking the SMT solver for 1 pairs
No discrepancies found
If however we replace the
PUSH32 0x0
with
PUSH32 0xffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffff
we get:
$ hevm equivalence --code-a "60003560000260005260016000f3" --code-b "7fffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffff60005260016000f3"
Found 1 total pairs of endstates
Asking the SMT solver for 1 pairs
Reuse of previous queries was Useful in 0 cases
Not equivalent. The following inputs result in differing behaviours:
-----
Calldata:
Empty
Which shows that even with empty calldata, the two are not equivalent: one
returns 0xff and the other 0x0.
Symbolic Execution Tutorial
Symbolic execution mode of hevm checks whether any call to the contract could result in an assertion violation. Let's see a simple contract, in file contract-symb-1.sol:
//SPDX-License-Identifier: MIT
pragma solidity ^0.8.19;
contract MyContract {
function simple_symb() public pure {
uint i;
i = 1;
assert(i == 2);
}
}
Let's first compile it with solc:
$ solc --bin-runtime contract-symb-1.sol
======= contract-symb-1.sol:MyContract =======
Binary:
6080604052348015600e575f80f....
Now let's symbolically execute it:
$ hevm symbolic --sig "simple_symb()" --code "6080604052348015...."
Discovered the following counterexamples:
Calldata:
0x881fc77c
Storage:
Addr SymAddr "miner": []
Addr SymAddr "origin": []
Transaction Context:
TxValue: 0x0
Symbolically executing a specific function
When there are more than one functions in the code, the system will try to symbolically execute all. Let's take the file contract-symb-2.sol:
//SPDX-License-Identifier: MIT
pragma solidity ^0.8.19;
contract MyContract {
uint i;
function simple_symb1() public view {
assert(i == 2);
}
function simple_symb2() public view {
assert(i == 3);
}
}
And compile it with solc:
$ solc --bin-runtime contract-symb-2.sol
======= contract-symb-2.sol:MyContract =======
Binary of the runtime part:
6080604052348015600e57....
Now execute the bytecode symbolically with hevm:
$ hevm symbolic --code "608060405234...."
Discovered the following counterexamples:
Calldata:
0x85c2fc71
Storage:
Addr SymAddr "entrypoint": [(0x0,0x0)]
Addr SymAddr "miner": []
Addr SymAddr "origin": []
Transaction Context:
TxValue: 0x0
Calldata:
0x86ae3309
Storage:
Addr SymAddr "entrypoint": [(0x0,0x0)]
Addr SymAddr "miner": []
Addr SymAddr "origin": []
Transaction Context:
TxValue: 0x0
Notice that hevm discovered two issues. The calldata in each case is the function
signature that cast from foundry gives for the two functions:
$ cast sig "simple_symb1()"
0x85c2fc71
$cast sig "simple_symb2()"
0x86ae3309
In case you only want to execute only a particular function, you can ask hevm
to only execute a particular function signature via the --sig option:
$ hevm symbolic --sig "simple_symb1()" --code "6080604052348015600...."
Discovered the following counterexamples:
Calldata:
0x85c2fc71
Storage:
Addr SymAddr "entrypoint": [(0x0,0xffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffffff)]
Addr SymAddr "miner": []
Addr SymAddr "origin": []
Abstract versus empty starting storage
The initial store state of hevm is completely abstract. This means that the
functions are explored for all possible values of the state. Let's take the
following contract contract-symb-3.sol:
//SPDX-License-Identifier: MIT
pragma solidity ^0.8.19;
contract MyContract {
uint i;
function simple_symb() public view {
assert(i == 0);
}
}
Let's compile with solc:
solc --bin-runtime contract-symb-3.sol
======= contract-symb-3.sol:MyContract =======
Binary of the runtime part:
6080604052348015600e575f80fd5b50600436106026575f3560e01c806388....
With default symbolic execution, a counterexample is found:
$ cabal hevm symbolic --initial-storage Empty --code "60806040523...."
Discovered the following counterexamples:
Calldata:
0x881fc77c
Storage:
Addr SymAddr "entrypoint": [(0x0,0x1)]
Addr SymAddr "miner": []
Addr SymAddr "origin": []
Transaction Context:
TxValue: 0x0
However, notice that the counterexample has 1 as the value for i storage
variable. However, this contract can never actually assign i to any value.
Running this contract with --initial-state Empty ensures that the default
value, 0, is assigned, and the assert can never fail:
cabal run exe:hevm -- symbolic --initial-storage Empty --code "60806040...."
QED: No reachable property violations discovered
Here, no counterexamples are discovered, because with empty default state, the
value of i is zero, and therefore assert(i == 0) will all never trigger.
Using forge to build your project for symbolic execution
Forge can also be used to build your project and run symbolic execution on it.
This fits in well with standard development practices. You can use forge to
build and then jq to extract the runtime bytecode. Let's say we have the
following contract:
contract AbsStorage {
uint256 public a;
function not2() public {
assert(a != 2);
}
}
Notice that this contract cannot set a to 2, hence the assert will never fail
in the real world. However, in symbolic mode, hevm allows the state to be
symbolic, hence it can explore all possible values of a, even ones that are
not possible in the real world. Let's compile this contract with forge and then
run symbolic execution on it:
$ forge build --ast
[⠒] Compiling...
[⠢] Compiling 1 files with Solc 0.8.19
[⠆] Solc 0.8.19 finished in 11.46ms
$ hevm symbolic --code $(jq -r '.deployedBytecode.object' out/abs_storage.sol/AbsStorage.json )
Discovered the following 1 counterexample(s):
Calldata:
0xb1712ffd
Storage:
Addr SymAddr "entrypoint": [(0x0,0x2)]
Addr SymAddr "miner": []
Addr SymAddr "origin": []
Transaction Context:
TxValue: 0x0
The calldata provided by hevm is the function signature of not2(). This can
be checked via cast, which is installed as part of foundry:
cast keccak "not2()"
0xb1712ffd...
We can get all the details of the state and context led to the counterexample
by using the --get-models flag. While there will be a number of branches
displayed, only one will be relevant to the counterexample. Here is the
relevant branch:
=== Models for 8 branches ===
[...]
--- Branch ---
Inputs:
Calldata:
0xb1712ffd
Storage:
Addr SymAddr "entrypoint": [(0x0,0x2)]
Transaction Context:
TxValue: 0x0
End State:
(Failure
Error:
(Revert
(ConcreteBuf
Length: 36 (0x24) bytes
0000: 4e 48 7b 71 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 NH{q............
0010: 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 ................
0020: 00 00 00 01 ....
)
)
[...]
Here, the storage variable is set to 2, which is the value that
the assert tested for. Notice that the panic exception is of type 01, which
is what's expected for an assert failure in
solidity.
hevm test
Usage: hevm test [--root STRING] [--project-type PROJECTTYPE] [--rpc TEXT]
[--number W256] [--verb INT] [--match STRING]
[--solver TEXT] [--num-solvers NATURAL] ...
Execute all unit tests that make use of the std-test assertion library
a.k.a Foundry tests on functions that
start with prove_. This command supports both Foundry- and
Dapptools-based projects. For a full listing of options,
see hevm test --help. For common options, see here.
Simple example usage
If you are inside a forge project that has already been built via forge build --ast, you can:
$ hevm test
Checking 1 function(s) in contract src/badvault-test.sol:BadVault
[RUNNING] prove_mytest(uint256)
[PASS] prove_mytest(uint256)
To prove all function that start with prove_ in all contracts.
Further reading
See our
tutorial here for more details. An overview of using
std-test for solidity testing can be found in the foundry
book.
hevm symbolic
Usage: hevm symbolic [--code TEXT] [--code-file STRING] [--calldata TEXT] [--address ADDR]
[--caller ADDR] [--origin ADDR] [--coinbase ADDR]
[--value W256] [--nonce WORD64] [--gas WORD64]
[--number W256] [--timestamp W256] [--basefee W256] ...
Run a symbolic execution against the given parameters, searching for assertion
violations. For a full listing of options, see hevm symbolic --help.
For common options, see here.
Counterexamples are returned for any reachable assertion violations. Where
an assertion violation is defined as either an execution of the invalid opcode
(0xfe), or a revert with a message of the form
abi.encodeWithSelector('Panic(uint256)', errCode) with errCode being one of
the predefined solc assertion codes defined
here.
Arithmetic overflow
By default hevm ignores assertion violations that result from arithmetic
overflow (Panic(0x11)), although this behaviour can be customised via the
--assertions flag. For example, the following will return counterexamples for
arithmetic overflow (0x11) and user defined assertions (0x01):
hevm symbolic --code $CODE --assertions '[0x01, 0x11]'
The default value for calldata and caller are symbolic values, but can be
specialized to concrete functions with their corresponding flags.
Specializing calldata
One can also specialize specific arguments to a function signature, while
leaving others abstract. If --sig is given, calldata is assumed to be of the
form suggested by the function signature. With this flag, specific arguments
can be instantiated to concrete values via the --arg flag.
This is best illustrated through a few examples:
Calldata specialized to the bytestring 0xa9059cbb followed by 64 symbolic bytes:
hevm symbolic --sig "transfer(address,uint256)" --code $(<dstoken.bin-runtime)
Calldata specialized to the bytestring
0xa9059cbb0000000000000000000000007cfa93148b0b13d88c1dce8880bd4e175fb0dedf
followed by 32 symbolic bytes.
hevm symbolic --sig "transfer(address,uint256)" --arg 0x7cFA93148B0B13d88c1DcE8880bd4e175fb0DeDF --code $(<dstoken.bin-runtime)
Calldata specialized to the bytestring 0xa9059cbb followed by 32 symbolic
bytes, followed by the bytestring
0000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000:
hevm symbolic --sig "transfer(address,uint256)" --arg "<symbolic>" --arg 0 --code $(<dstoken.bin-runtime)
If the --get-models flag is given, example input values will be returned for
each possible execution path. This can be useful for automatic test case
generation.
The default timeout for SMT queries is no timeout. If your program is taking
longer than a couple of minutes to run, you can experiment with configuring the
timeout to somewhere around 10s by doing --smttimeout 10000
Storage
Storage can be initialized in two ways:
Empty: all storage slots for all contracts are initialized to zeroAbstract: all storage slots are initialized as unconstrained abstract values
Exploration strategy
hevm uses an eager approach for symbolic execution, meaning that it will
first attempt to explore all branches in the program (without querying the smt
solver to check if they are reachable or not). Once the full execution tree has
been explored, the postcondition is checked against all leaves, and the solver
is invoked to check reachability for branches where a postcondition violation
could occur. While our tests have shown this approach to be significantly
faster, when applied without limits it would always result in infinite
exploration of code involving loops, so after some predefined number of
iterations (controlled by the --ask-smt-iterations flag), the solver will be
invoked to check whether a given loop branch is reachable. In cases where the
number of loop iterations is known in advance, you may be able to speed up
execution by setting this flag to an appropriate value.
Further reading
For a tutorial on symbolic execution with hevm, see the the page
here.
An older blog post on symbolic execution with hevm can be found
here.
hevm equivalence
Usage: hevm equivalence [--code-a TEXT] [--code-b TEXT] [--code-a-file STRING]
[--code-b-file STRING] [--sig TEXT] [--arg STRING]...
[--calldata TEXT] [--smttimeout NATURAL]
[--max-iterations INTEGER] [--solver TEXT]
[--num-solvers NATURAL] ...
Symbolically execute both the code given in --code-a and --code-b and try
to prove equivalence between their outputs and storages. For a full listing of
options, see hevm equivalence --help. For common options, see
here.
Simple example usage
Let's set contract1.sol to:
contract MyContract {
mapping (address => uint) balances;
function my_adder(address recv, uint amt) public {
if (balances[recv] + amt >= 100) { revert(); }
balances[recv] += amt;
}
}
And let's set contract2.sol to:
contract MyContract {
mapping (address => uint) balances;
function my_adder(address recv, uint amt) public {
if (balances[recv] + amt >= 100) { revert(); }
balances[recv] += amt/2;
balances[recv] += amt/2;
}
}
Then we can check if they are equivalent by running:
solc --bin-runtime "contract1.sol" | tail -n1 > a.bin
solc --bin-runtime "contract2.sol" | tail -n1 > b.bin
hevm equivalence --code-a-file a.bin --code-b-file b.bin
Calldata size limits
If --sig is given, calldata is assumed to take the form of the function
given. If --calldata is provided, a specific, concrete calldata is used. If
neither is provided, a fully abstract calldata of at most 2**64 byte is
assumed. Note that a 2**64 byte calldata would go over the gas limit, and
hence should cover all meaningful cases. You can limit the buffer size via
--max-buf-size, which sets the exponent of the size, i.e. 10 would limit the
calldata to 2**10 bytes.
What constitutes equivalence
The equivalence checker considers two contracts equivalent if given the same calldata they:
- return the same value
- have the same storage
- match on the success/failure of the execution
Importantly, logs are not considered in the equivalence check. Hence,
it is possible that two contracts are considered equivalent by
hevm equivalencebut they emit different log items. Furthermore, gas is explicitly not considered, as in many cases, the point of the equivalence check is to ensure that the contracts are functionally equivalent, but one of them is more gas efficient.
For example, two contracts that are:
PUSH1 3
And
PUSH1 4
Are considered equivalent, because they don't put anything in the return data, are not different in their success/fail attribute, and don't touch storage. However, these two are considered different:
PUSH1 3
PUSH1 0x20
MSTORE
PUSH1 0x40
PUSH1 0x00
RETURN
and:
PUSH1 4
PUSH1 0x20
MSTORE
PUSH1 0x40
PUSH1 0x00
RETURN
Since one of them returns a 3 and the other a 4. We also consider contracts different when they differ in success/fail. So these two contracts:
PUSH1 0x00
PUSH1 0x00
RETURN
and:
PUSH1 0x00
PUSH1 0x00
REVERT
Are considered different, as one of them reverts (i.e. fails) and the other succeeds.
Creation code equivalence
If you want to check the equivalence of not just the runtime code, but also the
creation code of two contracts, you can use the --creation flag. For example
the following two contracts compare equal when compared with --create flag.
Let's set the first contract to create1.sol:
contract C {
uint private immutable NUMBER;
constructor(uint a) {
NUMBER = 2;
}
function stuff(uint b) public returns (uint256) {
unchecked {return 2+NUMBER+b;}
}
}
And the second contract to create2.sol:
contract C {
uint private immutable NUMBER;
constructor(uint a) {
NUMBER = 4;
}
function stuff(uint b) public returns (uint256) {
unchecked {return NUMBER+b;}
}
}
And let's compare them via --create:
solc --bin create1.sol | tail -n1 > create1.bin
solc --bin create2.sol | tail -n1 > create2.bin
hevm equivalence --code-a-file create1.bin --code-b-file create2.bin --create
Notice that we used --bin and not --bin-runtime for solc here. Also note that
in case NUMBER is declared public, the two contracts will not be considered
equivalent, since solidity will generate a getter for NUMBER, which will
return 2/4 respectively.
Further reading
For a tutorial on how to use hevm equivalence, see the equivalence checking
tutorial.
hevm exec
Run an EVM computation using specified parameters.
Usage: hevm exec [--code ARG] [--code-file ARG] [--project-type ARG] [--create]
[--json-trace] [--address ARG] [--caller ARG] [--origin ARG]
[--coinbase ARG] [--value ARG] [--nonce ARG] [--gas ARG]
[--number ARG] [--timestamp ARG] [--basefee ARG]
[--priority-fee ARG] [--gaslimit ARG] [--gasprice ARG]
[--maxcodesize ARG] [--prev-randao ARG] [--chainid ARG]
[--rpc ARG] [--block ARG] [--ask-smt-iterations ARG]
[--loop-detection-heuristic ARG] [--no-decompose]
[--solver ARG] [--debug] [--calldata ARG] [--trace]
[--verb ARG] [--root ARG] [--assertion-type ARG]
[--smt-timeout ARG] [--smt-memory ARG] [--smtdebug]
[--dump-unsolved ARG] [--num-solvers ARG]
[--max-iterations ARG] [--promise-no-reent]
[--max-buf-size ARG] [--max-width ARG] [--max-depth ARG]
[--no-simplify] [--only-deployed] [--cache-dir ARG]
Concretely execute a given EVM bytecode with the specified parameters. Minimum
required flags: either you must provide --code or you must both pass --rpc
and --address. For a full listing of options, see hevm exec --help.
If the execution returns an output, it will be written to stdout. Exit code indicates whether the execution was successful or errored/reverted.
Simple example usage
$ hevm exec --code 0x647175696e6550383480393834f3 --gas 0xff
"Return: 0x647175696e6550383480393834f3"
Which says that given the EVM bytecode 0x647175696e6550383480393834f3, the Ethereum
Virtual Machine will put 0x647175696e6550383480393834f3 in the RETURNDATA.
To execute a mainnet transaction:
$ export ETH_RPC_URL=https://mainnet.infura.io/v3/YOUR_API_KEY_HERE
$ export TXHASH=0xd2235b9554e51e8ff5b3de62039d5ab6e591164b593d892e42b2ffe0e3e4e426
hevm exec --caller $(cast tx $TXHASH from) --address $(cast tx $TXHASH to) \
--calldata $(cast tx $TXHASH input) --rpc $ETH_RPC_URL \
--block $(($(cast tx $TXHASH blockNumber)-1)) --gas $(cast tx $TXHASH gas)
Common options
The subcommands of hevm present a number of common options. Here, we document these options in detail.
Maximum Buffer Size, --max-buf-size
The buffers in hevm are limited to a maximum size of 2^N bytes, where N is by
default 64, but adjustable via the --max-buf-size flag. This helps to prevent
the system from creating buffers that are too large and would exceed the gas
limit. Limiting this value further to e.g. 20 can help to force the system to
generate counterexamples that are easier to examine and understand.
Choice of Solver, --solver
hevm can use any SMT solver that supports the AUFBV theory and incremental solving. Currently, z3, cvc5, and bitwuzla's interfaces are implemented. While any of these solvers work, we recommend using bitwuzla as it is in general extremely fast, almost always significantly faster than e.g. z3.
Number of Solvers, --num-solvers
hevm can run multiple solvers in parallel and will run as many solvers as it
detects the number of CPU cores on the machine. However, in some cases, that
may lead to memory outs, in case the solver happens to get queries that are
memory-intensive. In these cases, the number of solvers can be limited to a a
specific (low) number via the --num-solvers flag.
Promising no reentrancy, --promise-no-reent
hevm can be instructed to assume that no reentrancy will occur during the
execution of the contract. This is currently neccessary to fully explore
certain contracts. This is because value transfer is usually done via a CALL,
which can be reentrant. By promising no reentrancy, the system can assume that
no reentrancy will occur and can explore the contract more fully.
Timeout for SMT queries, --smttimeout
Some queries take too long. With a timeout, we ensure that hevm eventually
terminates. However, endstates where the timeout was reached are considered
inditerminate, and will lead to a WARNING in the output. It is worthwhile
trying to switch to a different SMT solver such as bitwuzla, or increasing the
timeout if this happens.
Loop Iteration Limit, --ask-smt-iterations
Loops in the code cause a challenge to symbolic execution framework. In order
to not run indefinitely, hevm will only explore a certain number of iterations
of a loop before consideing abandoning the exploration of that branch. This
number can be set via the --ask-smt-iterations flag.
Maximum Branch Width Limit, --max-width
Limits the number of potential concrete values that are explored in case a symbolic value is encountered, thus limiting branching width. For example, if a JUMP instruction is called with a symbolic expression, the system will explore all possible valid jump destinations, which may be too many. This option limits the branching factor in these cases. Default is 100.
If there are more than the given maximum number of possible values, the system
will try to deal with the symbolic value, if possible, e.g. via
over-approximation. If over-approximation is not possible, symbolic execution
will terminate with a Partial node, which is often displayed as "Unexpected
Symbolic Arguments to Opcode" to the user when e.g. running hevm test.
Maximum Branch Depth Limit, --max-depth
Limits the number of branching points on all paths during symbolic execution.
This is helpful to prevent the exploration from running for too long. Useful in
scenarios where you use e.g. both symbolic execution and fuzzing, and don't
want the symbolic execution to run for too long. It will often read to
WARNING-s related to Branches too deep at program counter.
General overview
To get an idea about what hevm is, see CAV'24 paper.
You can also check out a few presentations by @msooseth.
Debugging
Printf-style debugging
Haskell offers a way to print messages anywhere in the code with Debug.Trace.
The simplest is trace which takes a string and a value and returns the same value while printing the string.
For example
add x y = trace "Hello from add!" (x + y)
Testing
hevm uses Tasty framework for running tests, including QuickCheck for property-based testing. It also uses tasty-bench for benchmarking.
Running tests
The basic command to run the tests is:
cabal run test
For development, it might be beneficial to pass devel flag:
cabal run -f devel test
This should enable parallel compilation and test runs (see the config file hevm.cabal).
Additional parameters can be passed to the test runner after --. For example cabal run test -- --help will list all the additional parameters.
Some of the interesting options are -p <PATTERN> to filter only some of the tests and --quickcheck-tests <NUMBER> to control how many tests quickcheck will generate for each property test.
On property-based testing
There are a few ways to control how many tests Quickcheck will generate per property.
By default, it generates 100 tests (satisfying the precondition).
This can be controlled by maxSuccess argument passed to Quickcheck, or, in Tasty framework, using localOption (QuickCheckTests <N>).
Passing --quickcheck-tests <N> to the binary will change this value to <N>.
This value can be dynamically adjusted for a test group or a specific test.
For example, instead of localOption it is possible to use adjustOption for a test group.
The following ensures that for the following test group, the maximal value of the QuickCheckTests option is 50 (but if the current value is lower, it will be left unchanged).
adjustOption (\(Test.Tasty.QuickCheck.QuickCheckTests n) -> Test.Tasty.QuickCheck.QuickCheckTests (min n 50))
Similarly, the maxSuccess value can be modified for a single test. The following sets the number of tests generated to 20 for the particular test:
testProperty <property_name> $ withMaxSuccess 20 $ ...
Running benchmarks
You can also measure and compare the performance across hevm versions using the benchmarks.
bench-perf focuses on concrete execution performance, and bench is aimed at
symbolic execution and solving. Refer to the tasty-bench documentation for more detailed
usage information.
# Measure time and memory usage
$ cabal run bench-perf -- +RTS -T
# Collect timings for a base version
$ cabal run bench-perf -- --csv baseline.csv
# Perform some changes on the hevm code
# ...
# Benchmark changed code and compare with baseline
$ cabal run bench-perf -- --baseline baseline.csv
Profiling
Profiling Haskell code
NOTE: Most of the time will likely be spent in the solver, and that will not show up when profiling Haskell application.
In order to build the application with profiling information, we need to pass --enable-profiling to cabal.
If we want to profile the test suite, we could run
cabal run test --enable-profiling -- +RTS -p
Note that +RTS means the next arguments will be passed to GHC and -p instructs the program to create a time profile report.
This report is written into the .prof file.
If we want to pass arguments to our executable, we have to indicate this with -RTS, for example, to profile run of only some tests, we would use
cabal run test --enable-profiling -- +RTS -p -RTS -p <test_to_profile>
Steppers & Interpreters
The core EVM semantics in hevm can be found in EVM.hs. EVM state is contained
in the VM record, and the exec1 function executes a single opcode inside
the monad type EVM a = State VM a.
The core semantics are pure, and should information from the outside world be
required to continue execution (RPC queries or SMT queries),
execution will halt, and the result field of the VM will be an instance of
VMFailure (Query _).
Multiple steps of EVM execution are orchestrated via interpreters for a meta
language. Programs in the meta language are called Steppers. The instructions
in the meta language can be found in Stepper.hs.
There can potentially be many different interpreters with different features. Currently, we provide a concrete and a symbolic interpreter. Interpreters can handle Queries in different ways, for example in the symbolic interpreter, both sides of a branch point will be explored, while in the concrete interpreter, such branching is not permitted.
Interpreters are parametrized by a Fetcher that can handle RPC and SMT
queries, and can be instantiated with fetchers that could have different
fetching strategies (e.g. caching). Interpreters execute Steppers and use their
Fetcher to handle any Queries that need to be resolved.
This architecture is very modular and pluggable, and allows the core semantics to be shared between different interpreters, as well as the reuse of steppers between different interpreters, making it easy to e.g. share the same test execution strategy between concrete and symbolic interpreters.
graph LR
subgraph meta-language
A[Stepper]
end
subgraph interpreters
A --> B[Concrete]
A --> C[Symbolic]
end
subgraph fetchers
F[Fetch.hs]
B --> F
C --> F
end
subgraph EVM Semantics
G[EVM.hs]
B --> G
C --> G
end
Expr
The symbolic execution features in hevm are built using a custom IR,
imaginatively named Expr. This is a summarized trace semantics of a given
EVM program.
One important principle is that of local context: e.g. each term representing a read from a Buf/Storage will always contain a snapshot of the state of the buffer/store at the time the read occurred. This ensures that all context relevant to a given operation is contained within the term that represents that operation, and allows subsequent analysis to be stateless.
Expressions in this language can have the following types:
End: control flowWord: a 256 bit word (a stack item)Byte: a single byteBuf: a byte array (used for calldata, memory and returndata)Storage: contract storageLogs: EVM logs
Control Flow
An EVM program is represented by an [Expr End], which is a list of all
possible end states for a program. As an example the following
two Expr End-s encode a program that branches based on the equality of two symbolic
words ("a" and "b"), and returns if they are equal and reverts if they are not:
[ Success [PEq (Var "a") (Var "b")] ...,
, Failure [PNeg (PEq (Var "a") (Var "b"))] ...]
Buffers
Memory, calldata, and returndata are all represented as a Buf. Semantically speaking a Buf is a byte array with of size 2^256.
Bufs have three base constructors:
- AbstractBuf: all elements are fully abstract values
- ConcreteBuf bs: all elements past (length bs) are zero
Bufs can be read from with:
- ReadByte idx buf: read the byte at idx from buf
- ReadWord idx buf: read the byte at idx from buf
Bufs can be written to with:
- WriteByte idx val buf: write val to idx in buf
- WriteWord idx val buf: write val to idx in buf
- CopySlice srcOffset dstOffset size src dst: overwrite dstOffset -> dstOffset + size in dst with srcOffset -> srcOffset + size from src
e.g. the following Buf expression represents an abi encoded call to foo(uint256 a):
(WriteWord (Lit 0x4) (Var "a")
(WriteByte (Lit 0x3) (LitByte 56)
(WriteByte (Lit 0x2) (LitByte 189)
(WriteByte (Lit 0x1) (LitByte 190)
(WriteByte (Lit 0x0) (LitByte 47)
(AbstractBuf "txdata")))))
This represents calldata of the form:
-----------------------------------------------------------------------
| <function selector> | <symbolic word> | arbitrary symbolic data.... |
-----------------------------------------------------------------------
Note that a Buf expression contains a copy of all historical writes, meaning that it is possible to write multiple times to the same location. In this case only the topmost write is relevant. This allows us to mix symbolic and concrete writes to the same buffer.
Storage
Storage expressions are similar, but instead of writing regions of bytes, we write a word to a particular key in a given addresses storage. Note that as with a Buf, writes can be sequenced on top of concrete, empty and fully abstract starting states.
As with Bufs, Storage expressions contain a full history of all previous writes.
For example the following expression represents a write of a symbolic word "c"
to slot 2 for the zero address followed by a write of 1 to the slot at the
symbolic location "b" for the zero address. These writes are sequenced on top
of an EmptyStore meaning all other storage locations are held to be 0.
(SStore (Lit 0) (Var "b") (Lit 1)
(SStore (Lit 0) (Lit 2) (Var "c")
EmptyStore))
Logs
Logs are also represented as a sequence of writes, but unlike Buf and Storage expressions, Log writes are always sequenced on an empty starting point, and overwriting is not allowed.
Symbolic Execution
During symbolic execution all possible branches of the program are explored symbolically. Reachability analysis is performed at this stage only if needed for loop unrolling. This produces an Expr End. As an example consider the following program:
contract MyContract {
mapping(uint => uint) items;
function test(uint val1) public {
require(val1 > 10);
unchecked {
items[4] = val1+1;
assert(items[4] > 10);
}
}
}
This decompiles into the following Expr End:
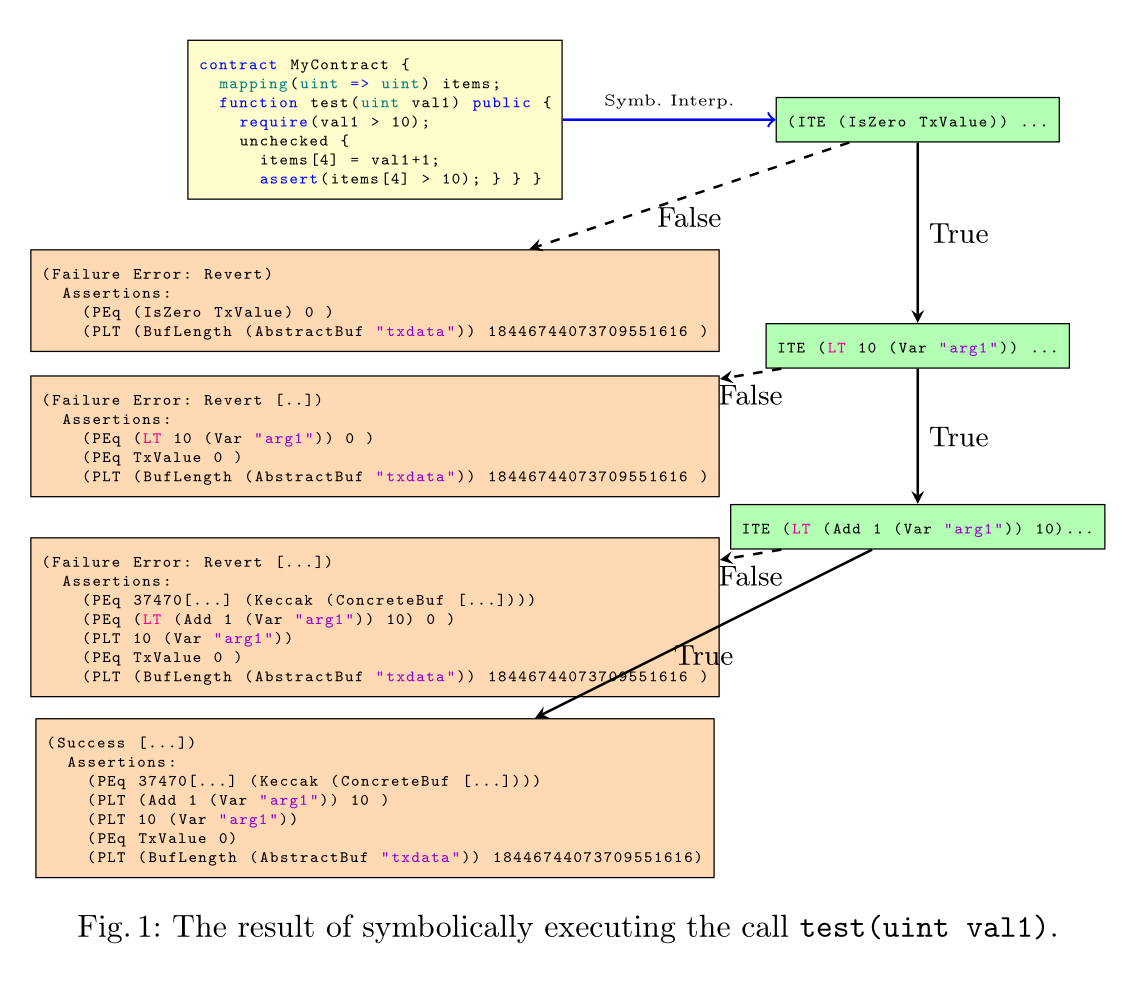
For more details, see our research paper on hevm on open access research paper as presented at CAV 2024, presentation here